Main Application
The figure shows which steps must be done for optimize an energy system model. At the bottom of the side bar you will find a button that deletes all stored data such as time series reduction values.
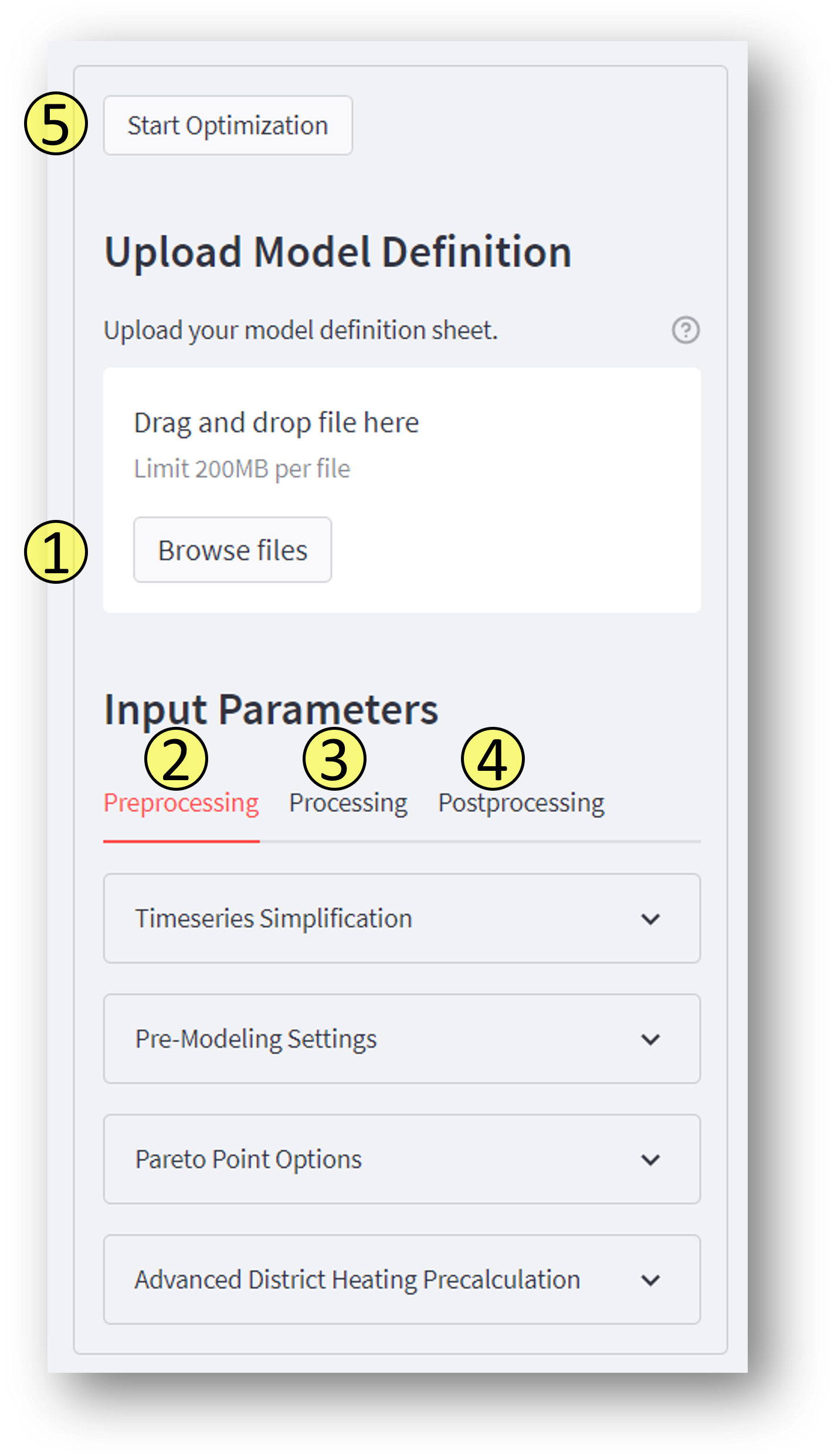
1. Adding the model definition
Here you can upload your model_definition.xlsx. After the file has been uploaded, you can theoretically continue with step 5. However, it is useful to make settings to reduce the computing time, since only limited computing resources are available.
2. Preprocessing
There are several ways to simplify the model. The method can be found here: Modeling Method. In the following, only the application is briefly described.
Timeseries Simplificaton
Warning
All time series simplifications can currently only be applied at an input time resolution of hours with 8760 time steps (i.e. one whole year). The algorithm described in the following sub-sections can be applied. Depending on the simplification applied, further adjustments to the energy system area automatically carried out.
Depending on which of the time series preparation algorithms described in the methods section is used, the following specifications must be made:
Algorithm: Indication of the simplification algorithm to be applied.
Index: Algorithm specific configuration.
Criterion: Criterion according to which cluster algorithms are applied.
Period: Time periods which are clustered together (weeks, days, hours)
Season: Time periods within which clustering takes place (year, seasons, months)
The following algorithms are applicable and must be specified with the following additional information. A detailed description of the algorithms can be found in the methods section.
algorithm |
description |
index |
criterion |
period |
season |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
k_means |
The k-means algorithm clusters the time periods (see period) in such a way; that the squared deviation of the cluster centers is minimal. From the time periods of one cluster the mean is calculated and returned as reference period of the cluster. For the decision the vector of a single parameter (see criterion) over the period duration is considered. |
number of clusters to be considered. The number of clusters equals the number of returned reference days. |
Clustering criterion to be considered (temperature; dhi; heat demand; electricity demand) |
Period length to be clustered (hours; days; or weeks) |
– |
averaging |
successive time periods (e.g. two consecutive days) are averaged and combined into one segment. |
number of periods to be averaged |
– |
length of periods to be averaged (hours; days; weeks) |
– |
slicing A |
every n-th period is selected and considered within the modeling |
index = n (every n-th period is selected in the modeling) |
– |
length of periods to be sliced (hours; days; weeks) |
– |
slicing B |
every n-th period is deleted and removed from the modeling |
index = n (every n-th period is removed) |
– |
length of periods to be sliced (hours; days; weeks) |
– |
downsampling A |
Adaption of the temporal resolution. Every n-th period (selected by index column) is used for the modeling. For example; the resolution can be changed from a 1-hourly to a 3-hourly (index = 3) temporal resolution [1]. |
index = n (setting the new resolution) |
– |
– |
– |
downsampling B |
Adaption of the temporal resolution. Every n-th period (selected by index column) is deleted for the modeling. |
index = n (determination of the time steps to be deleted) |
– |
– |
– |
heuristic selection |
representative time periods of a time series are selected from certain selection criteria |
applied selection scheme (available schemes are listed here |
– |
length of periods to be selected (days or weeks) |
– |
random sampling |
a given number of random periods are selected and used as representatives |
number of periods to be selected. |
– |
length of periods to be selected randomly (days or weeks |
– |
Pre-Modeling Settings
Activate Pre-Modeling: If activated, the modeling process is divided into a pre-model and a main-model run.
Investment Boundaries Tightening: Must be checked, if the investment boundaries in the main-model shall be tightened based on the pre-model results.
Investment Tightening Factor: All investment limits of the main-model are limited to the investment decisions made in the pre-model run multiplied by this factor. If a originally defined investment boundary is lower than this value, the limit will not be changed.
Time Series Simplification: Timeseries simplification for the pre-model have to be set (see above for detailed description).
Pareto Point Options
Choose pareto point(s) if you want to start an pareto optimization run. The chosen value defines the constraint reduction in percent referring to the cost minimal pareto point. The values are given in percent.
Advances District Heating Precalculation
Clustering District Heating Network: The function allows to group the consumers of a street section into a clustered consumer when optimizing the heat network. This consumer is positioned at the averaged location.
Activate District Heating Precalculations: With use of this function it is possible to use the result folder of a model definition after the first optimization to skip the perpendicular foot print search by using the already existing calculations (this is usually quite time-consuming). For this purpose, the result folder must be specified in the drop-down menu below.
Switch Criteria
If you activate this field, you set instead of the primary costs (e. g. monetary costs), the constraining costs (e. g. GHG-Emissions) as the optimization variable, so you perform an e. g. emission-optimized run. The field is intended for single-criteria optimization only. In case of multi-criteria optimization, the optimization criteria will be changed automatically.
3. Processing
Number of threads: Number of threads to use for the model run on your machine. You should make sure that the chosen solver supports enough threats (cbc: max. 1 (if no parallelized version), gurobi: max. 8).
Optimization Solver: Chose on of the supported solver. Make sure that the solver is configurated on your machine. We recommend using the gurobi solver if you can use an academic licence.
4. Postprocessing
Create xlsx-files: Must be checked, if you want to get result files of every bus. The field should only be checked if users have in-depth model knowledge.
5. Starting the optimization
The button starts the optimization. After the optimization process you will be automatically redirected to the Result Processing page.